Hoe ontstaat longfibrose?
Absolute contra-indicaties
Hoe ontstaat Longfibrose?
Longfibrose zorgt voor onomkeerbare schade aan de longblaasjes 1
Interstitiële longziekten (Interstitial Lung Diseases, ILD) is een verzamelnaam voor aandoeningen waarbij de ruimte rondom de longblaasjes (het interstitium) wordt aangetast. Longfibrose valt onder ILD, omdat er littekenweefsel in het interstitium ontstaat.1 Hoewel de onderliggende oorzaak van ILD kan verschillen, ontstaat en verloopt fibrosevorming vaak op een vergelijkbare manier.2–5
Figuur 1 laat de ontwikkeling van ILD-gerelateerde longfibrose zien.

Wanneer bedacht zijn op longfibrose?
Symptomen van longfibrose zijn onder andere:6–8
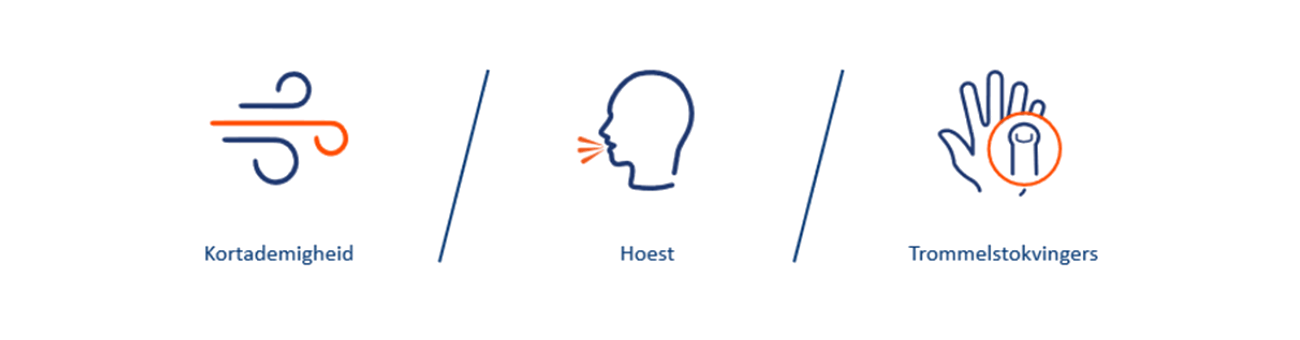
Patiënten kunnen ook last hebben van niet-specifieke symptomen of geen symptomen vertonen van hun ILD.9–12 Zelfs als er geen duidelijke tekenen zijn van longfibrose, kan het al voor onomkeerbare schade zorgen in de longen.9–11
Verkort de tijd tot diagnose: verwijs bij verdenking van ILD door naar een behandel- of expertisecentrum voor ILD.
REFERENCES:
-
Martinez FJ, Collard HR, Pardo A, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2017;3:17074. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2017.74
-
Cottin V, Hirani NA, Hotchkin DL, et al. Presentation, diagnosis and clinical course of the spectrum of progressive-fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Eur Respir Rev. 2018;27(150):180076. doi:10.1183/16000617.0076-2018
-
Bagnato G, Harari S. Cellular interactions in the pathogenesis of interstitial lung diseases. Eur Respir Rev. 2015;24(135):102 LP - 114. doi:10.1183/09059180.00003214
-
Kolb M, Vašáková M. The natural history of progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Respir Res. 2019;20(1):57. doi:10.1186/s12931-019-1022-1
-
Wuyts WA, Agostini C, Antoniou KM, et al. The pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis: a moving target. Eur Respir J. 2013;41(5):1207-1218. doi:10.1183/09031936.00073012
-
Molina-Molina M, Aburto M, Acosta O, et al. Importance of early diagnosis and treatment in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2018;12(7):537-539. doi:10.1080/17476348.2018.1472580
-
Raghu G, Remy-Jardin M, Richeldi L, et al. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (an Update) and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Adults: An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022;205(9):e18-e47. doi:10.1164/rccm.202202-0399ST
-
Oldham JM, Noth I. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Early detection and referral. Respir Med. 2014;108(6):819. doi:10.1016/J.RMED.2014.03.008
-
Spagnolo P, Ryerson CJ, Putman R, et al. Early diagnosis of fibrotic interstitial lung disease: challenges and opportunities. Lancet Respir Med. 2021;9(9):1065-1076. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00017-5
-
Ley B, Collard HR, King TE. Clinical Course and Prediction of Survival in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. https://doi.org/101164/rccm201006-0894CI. 2012;183(4):431-440. doi:10.1164/RCCM.201006-0894CI
-
Jeganathan N, Sathananthan M. Connective Tissue Disease-Related Interstitial Lung Disease: Prevalence, Patterns, Predictors, Prognosis, and Treatment. Lung 2020 1985. 2020;198(5):735-759. doi:10.1007/S00408-020-00383-W
-
Wallace B, Vummidi D, Khanna D. Management of Connective Tissue Diseases Associated Interstitial Lung Disease: A Review of the Published Literature. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2016;28(3):236. doi:10.1097/BOR.0000000000000270
PC-NL-106386
